PIPELIQ - Pressure and Mass Flow Balance in Hydraulic and Liquid Systems
Last Releases
2.4.5, March 2024
2.4.4, June 2022
2.4.1, May 2020
2.4.0, March 2019
Status
Commercial toolkit, available for sale and project development
Applications
Balances of pressures and mass flows of hydraulic/liquid systems
- Calculating pressure drops in piping networks
- Calculation of hydraulic balances (pressure and mass flow) in hydraulic systems
- Support in the sizing and selection of equipment (pumps, valves, pipes, etc.).
- Heat balances in non-compressible circuits
- Operation and control systems of non-compressible circuits: cooling loops and heat pipes with no phase change.
Description
PIPELIQ is a toolkit designed to perform balancing of pressures and mass flow of hydraulic/liquid systems. The toolkit considers thermal delay and thermal storage allowing the analysis of slow thermo-fluid transients. Moreover the user can design and tune the control loops of the fluid system due to the fact that fluid actuators and sensors can be connected to control elements.
The PIPELIQ toolkit provides a set of components to represent 1-D liquid flow networks. It enables the user to easily build typical simulation models of cooling and heating loops including the control system and to perform steady state, parametric studies and thermal transient studies of these models thanks to the powerful features of the EcosimPro/PROOSIS experiment.
This library can be used for different applications mainly focused on:
- Performing hydraulic balancing of pressures and mass flow
- Sizing and selection of equipment (pump, valves, pipes, etc)
- Thermal balances and thermal transient studies of 1-D liquid networks
Features
- The working fluid is a liquid which properties are calculated as function of the temperature
- Pressure loss in pipes and fittings are calculated using steady state correlations for pressure loss. Laminar and turbulent flow transition is taken into account
- Reverse flow
- Thermal storage in the fluid and solid walls of components
- Thermal delay due to convective transport can be simulated by nodalization of the pipes into multiple control volumes
- Hydrostatic pressure difference and natural circulation
- The simulation models can be connected to MS Excel
Limitations: PIPELIQ library does not consider the following phenomena:
- Two-phase flow overall as a result of boiling or fast drops in pressure
- Pressure waves (water hammer)
- Cavitation in valves and orifices
- Cavitation in pumps (a warning message is displayed when cavitation conditions are reached)
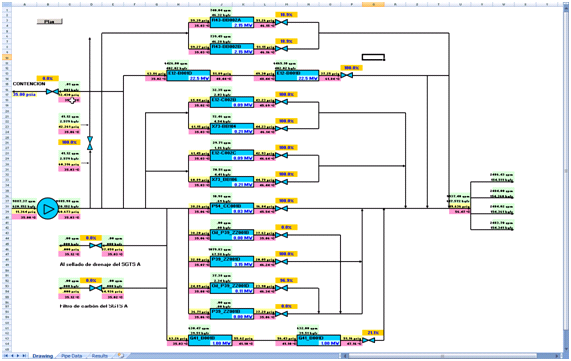
Flow distribution of an Essential Service Water System of a Nuclear Power Plant
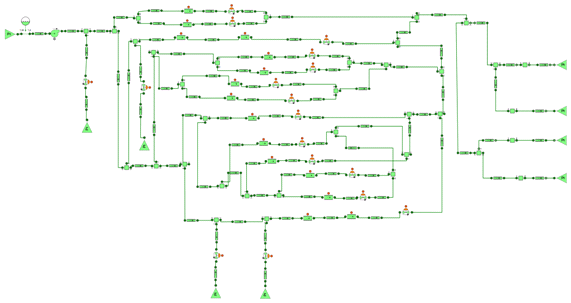
The purpose of this user case is to study the pressure balancing and the flow distribution of an Essential Service Water System of a Nuclear Power Plant. The following figure shows the schematics diagram of the model.
The model of this system was connected to MS Excel spreadsheet in order to easily report analyses changing the following parameters:
• Positions of the valves
• Thermal loads of the equipments
• Boundary conditions of the system (temperature, etc)
Low pressure feed water system of a Combined Cycle Power Plant
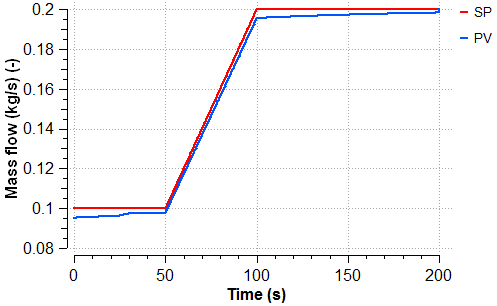
The model represents the low pressure feed water system of a combined cycle power plant. The model includes two pumps in parallel (the running one and the spare one) that provides water to the suppliers. Both pumping trains consider the minimum circulating flow and the attemperation water flow is regulated with a PI controller.
The schematics diagram of the simulation model is depicted in the following figure. This model shows the capability to include control logics of the hydraulic system.
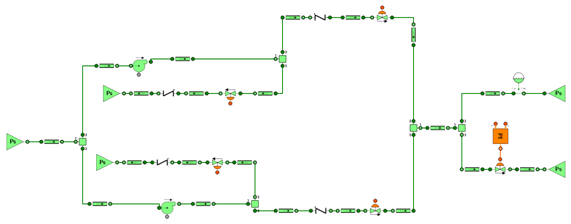
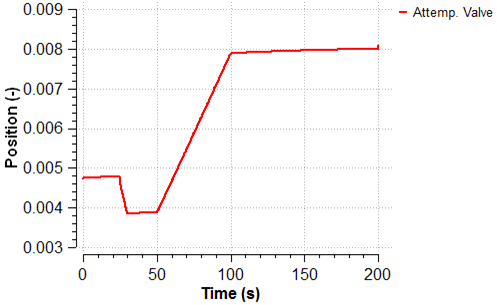
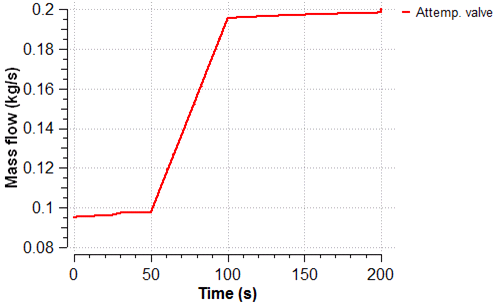
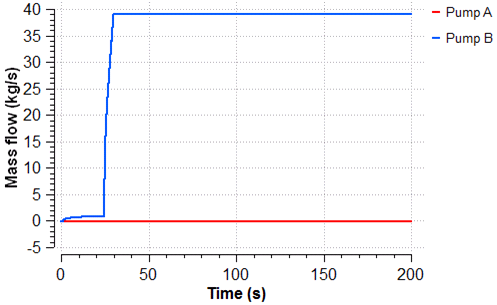
The scenario analyses the start-up of one of the pump according to a predefined start-up curve and the required attemperation water flow as a function of time using look-up tables.
The following plots show the evolution of the water flow supplied by the pump, the attemperation water flow, the behavior of the control loop and the position of the control valve during the start-up of the pump.
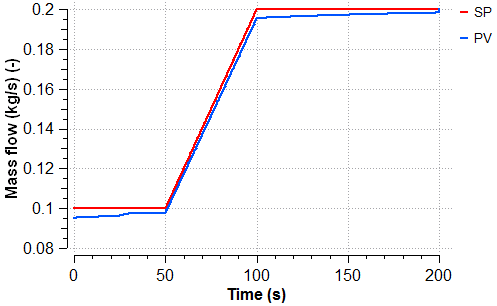
As the required mass flow across the atemperation line is greater, the valve is gradually opened as depicted in the following figure.